Access Control
Simplify Data Access Management for Databases and Data Lakes
Provision and manage access to all your data stores from any user, application, tool or service using your existing identity and access management (IAM) tools. Cyral helps organizations simplify data access management (DAM) and data democratization while embracing Zero Trust, without impacting user experience.
Before
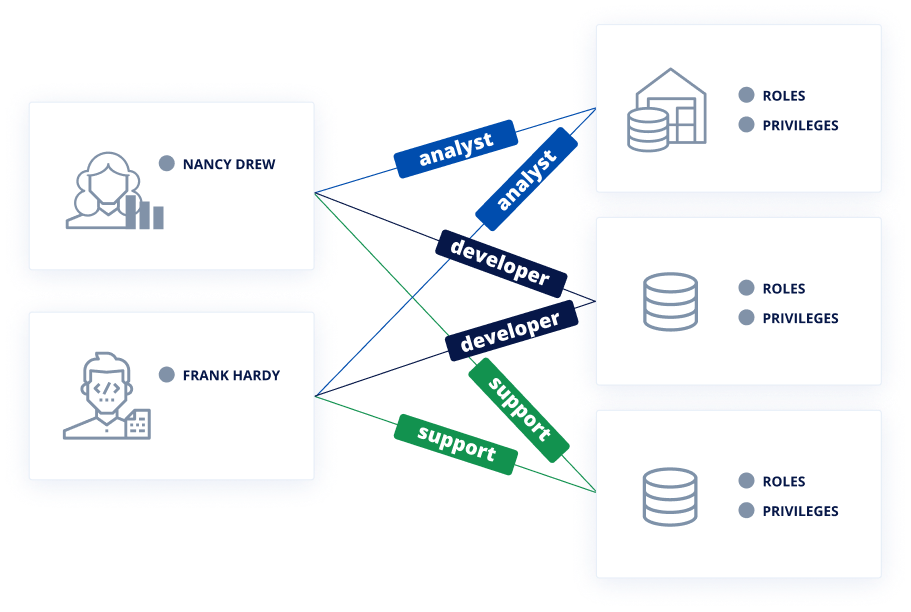

Before
Individual accounts are hard to manage at scale across data endpoints, many of which don’t support SSO protocols like SAML and OIDC. As a result, they are accessed using shared accounts.
- Ad hoc access provisioning
- Shared accounts and passwords
- Lack of visibility and compliance controls
After
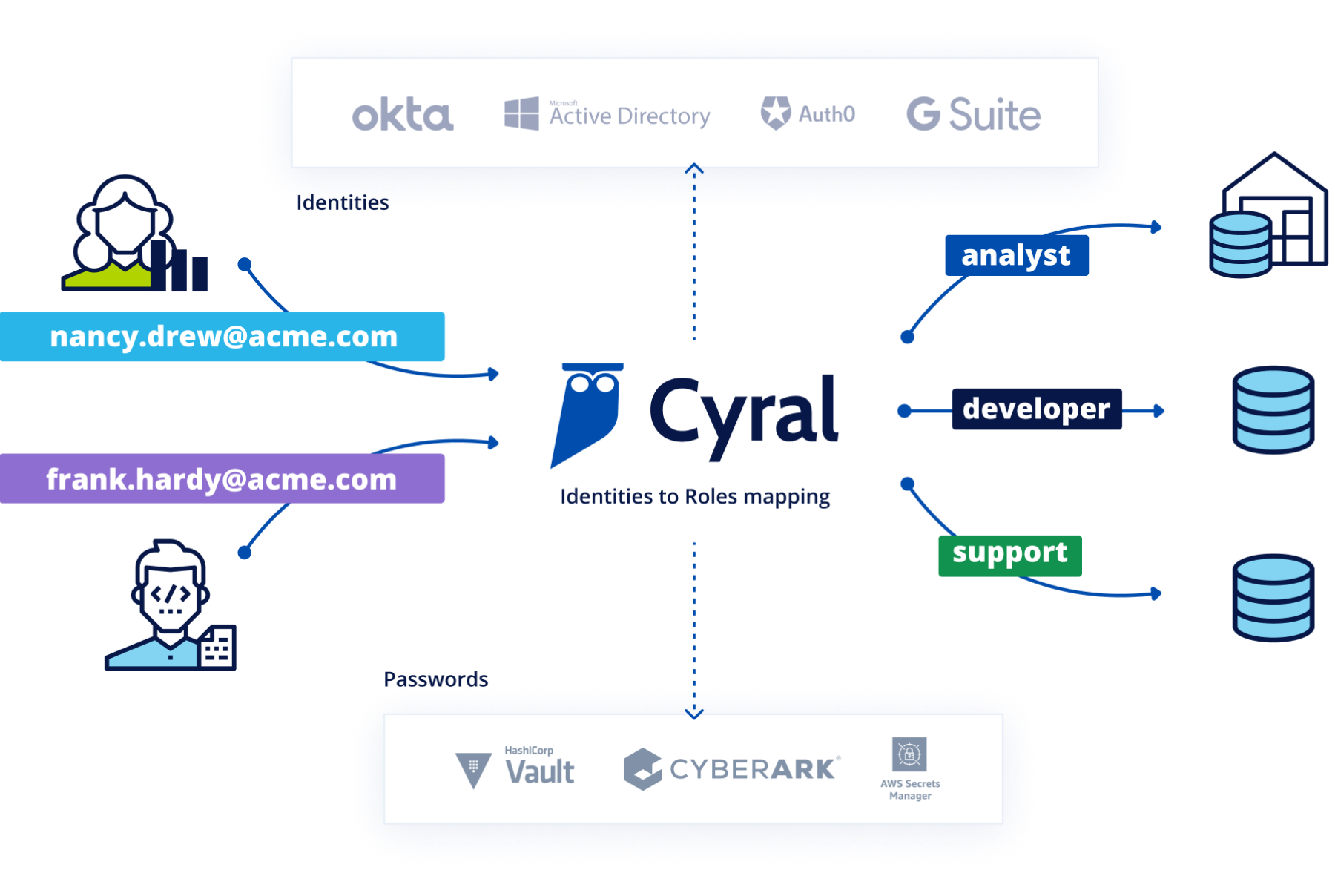


After
Cyral transparently intercepts requests to all data endpoints, and authenticates users with existing identity providers. Sessions that use service accounts are enriched with end user identity.
- Centralized and automated provisioning
- Unique credentials and password rotation
- Complete visibility and simple compliance controls
“Cyral was the missing piece for us in data access governance.”

Identity Federation
Data Access Management That’s Easy to Set Up
Data Access Management Benefits

Quickly and easily enable users to access cloud object storage without having to manage accounts in multiple places. Provision, delete, and reassign user access using groups defined in the Identity Provider of your choice.

Handle access for both web and client-based tools and applications. Enrich all activity data with user identity information, and apply access control policies uniformly, across all service accounts.

Leverage existing messaging and ticketing tools to enable ephemeral grants to users. Dynamically provision and manage access to privileged accounts needed for maintenance or troubleshooting.
Integrations
Terminology
Terminology
User Directories
A directory is a database of user information, such as their username, password (stored securely), fullname, and organizational groups to which they belong. It may be accessed either directly by a service or through an Identity Provider.
Identity Provider
An identity provider (IdP) authenticates a user and provides identity and access tokens for accessing other services. It uses SAML and OIDC protocols to interact with clients and is backed by a directory service storing user information.
Federation Services
Identity Provider Federation Services delegates authentication to one or more Identity Providers.
MFA Provider
A multi factor authentication (MFA) provider adds additional identity checks by requiring users to respond to a one-time password, an ephemeral token, or a push notification to an authorized device.
Secrets Manager
A secrets manager provides secure storage for sensitive passwords or credentials. Secrets managers often also have the ability to automatically rotate the passwords at periodic intervals.
Secrets Broker
A secrets broker delegates storage to an external secrets manager and interacts with it on behalf of a client.
IaC Tool
An infrastructure as code tool makes it possible to manage (create, update, delete) infrastructure (compute, storage, network, load balancers, etc.) as well as configuration data (init files, environment variables, policies, etc.) using a declarative model, and allows DevOps teams to use the same versioning and collaboration tools for their infrastructure and configuration as for their source code.
Least Privilege Access
The principle of least privilege (PoLP), also known as the principle of minimal privilege or the principle of least authority, recommends that users, systems, and processes only have access to resources (networks, systems, and files) that are absolutely necessary to perform their assigned function. With Cyral you can automatically limit access to production data services to only on-call engineers to ensure they only have access to the required resources to get their jobs done. Let on-call engineers grant limited access to others for troubleshooting and guarantee only just-enough access to ensure no disruptive actions are taken.
Database Activity Monitoring
Database Activity Monitoring (DAM) refers to any solution that is used to actively monitor and analyze database activity. This technology is multipurpose, typically being used by organizations both to fulfill specific compliance criteria, as well as protect their most sensitive data from external hackers and malicious insiders. For on-call access management this is important for having strong audit trails. This can help with meeting compliance needs particularly for organizations holding customer billing data where PCI Requirement 7 mandates that those organizations “limit access to system components and cardholder data to only those individuals whose job requires such access.” It can also support SOC2 as it relates to (a) limiting the number of users that have access to production systems and customer data, (b) capturing elaborate audit information about activity in production data systems.
Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management (PAM) refers to systems or services that can securely manage user accounts that have elevated permissions to critical systems, databases or resources. There are three types of privilege access management needs that most organizations use for on-call access management. Standing access, which most companies are trying to reduce because this poses data security and compliance risk. Rotating access, as is the case with on-call, which most companies are trying to operationalize and automate because of the overhead. And on-demand access, also described as breakglass or P0, which most companies don’t have tooling for handling. Cyral operationalizes and automates all three types of access, limits activity based on customer-defined policies, creates audit artifacts, and captures rich activity logs complete with user identity.
Ephemeral Credentials Manager
An ephemeral credentials manager issues short lived passwords for connecting to a service, thus obviating the need to store and rotate credentials.
Limitations of Native Access Management Controls in Data Warehouses, and How Cyral Helps
Read White PaperReady to Get Started?
Get started in minutes and explore how Cyral can protect your Data Mesh with Data Access Control. You can also contact us to see a live demo.



