Identity and Access Management
Identity and Access Management Definition
Identity and Access Management (IAM) refers to the policies, procedures, and technologies that enable an organization to manage the digital identities and access rights of its employees, contractors, partners, customers, and other stakeholders. IAM involves defining and enforcing access controls to ensure that only authorized individuals have access to the right resources, at the right time, and for the right reasons.
Identity and Access Management FAQs
What is Identity and Access Management
Identity and Access Management services typically implement four main processes: identification, authentication, authorization, and accountability. Identification involves establishing the identity of a user, while authentication verifies the user’s identity using one or more factors such as a password, smart card, or biometric data, such as facial recognition. Authorization determines the level of access that a user is granted based on their identity and other factors such as their job role or location. Accountability involves auditing and logging access to resources to ensure compliance with policies and regulations.
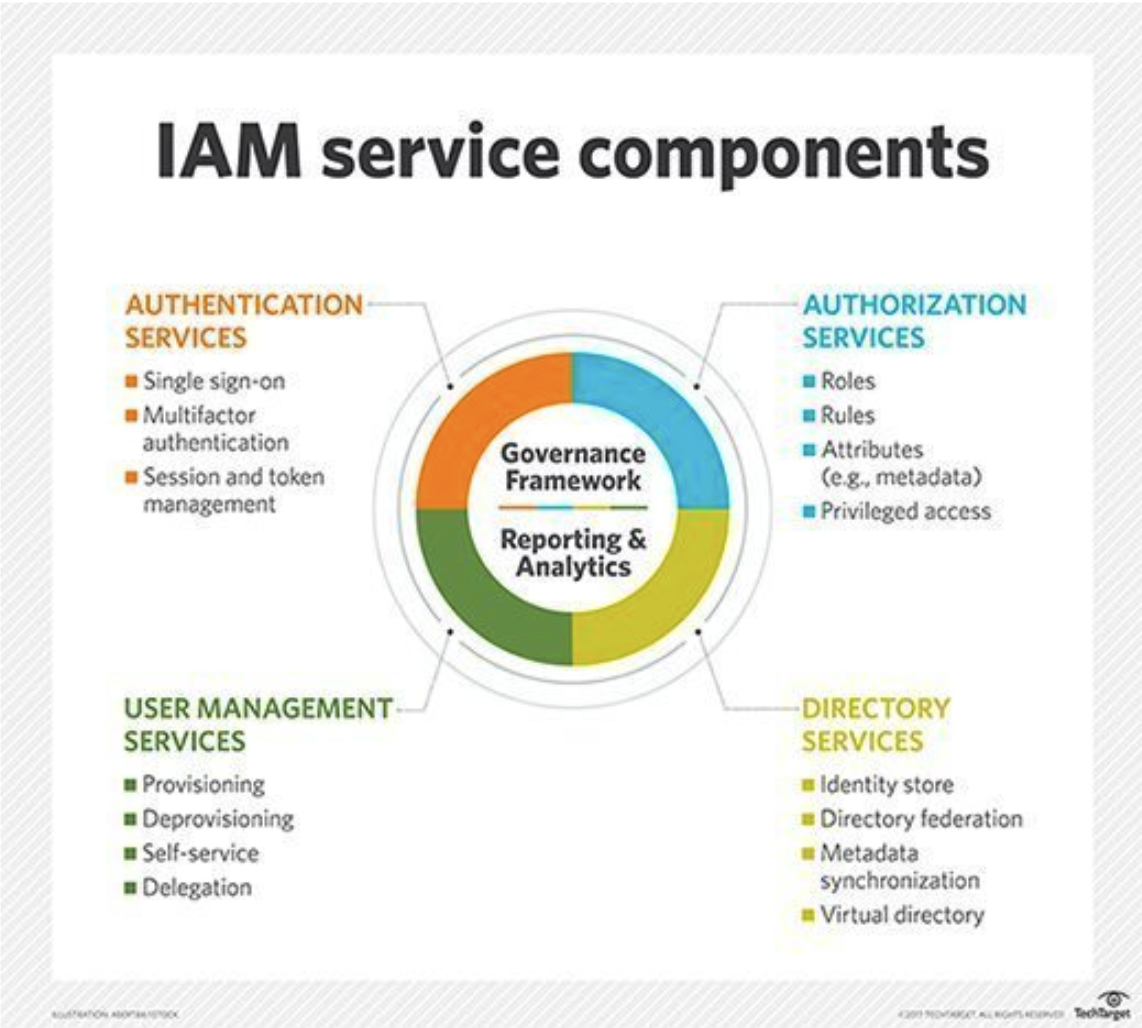
An identity and access management system can be complex, requiring coordination across multiple departments and technologies such as directories, identity providers, access management tools, and authentication systems. Effective access and identity management can help organizations reduce the risk of data breaches, streamline user access to resources, and improve compliance with regulatory requirements.
What is the Identity and Access Management Process?
There are several critical Identity and Access Management concepts that should be implemented, including:
- Identity Proofing: This step involves collecting and verifying the identity of a user before granting them access to resources. This can include verifying personal information such as name, address, and date of birth, as well as government-issued identification documents.
- User Authentication: After the user’s identity has been verified, they must authenticate themselves using one or more factors such as passwords, biometric data, or smart cards.
- Authorization: Once the user has been authenticated, an access and identity management system will determine what resources the user is authorized to access based on factors such as their job role, location, and other attributes. This process includes granting access to specific systems, applications, and data.
- Provisioning: After the user has been authorized, IAM systems provision access to resources, which involves creating user accounts and granting access permissions.
- Monitoring and Auditing: Cloud Identity Access and Management systems monitor user activity and audit access to resources to ensure compliance with policies and regulations. This includes logging access attempts, changes to user permissions, and other events related to user access.
- De-provisioning: When a user no longer needs access to resources or leaves the organization, IAM systems de-provision access by removing user accounts and revoking access permissions.
An effective identity and access manager will be able coordinate multiple departments and technologies such as directories, identity providers, access management tools, and authentication systems. Identity and access management systems must also be regularly reviewed and updated to ensure they remain effective in addressing changing data security threats and regulatory requirements.
The Importance of Identity and Access Management
Identity and Access Management tools are important for several reasons. The benefits of Identity and Access Management include:
Security
A thorough Identity and Access Management strategy helps to ensure that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive data and systems, reducing the risk of data breaches and other security incidents. It also helps to protect against internal threats, such as employees accessing or sharing sensitive data without authorization.
Compliance
Many industries are subject to regulatory requirements that mandate the protection of sensitive data and the establishment of access controls. IAM implementation helps organizations comply with these regulations by enforcing access controls and providing audit trails of access to sensitive data.
Productivity
IAM can improve productivity by streamlining the process of granting access to resources, reducing the time and effort required to manage user access.
Cost Savings
By automating the process of managing user access, IAM can reduce the cost of manual processes such as usernames and passwords resets and user provisioning.
Improved User Experience
IAM can provide users with a single sign-on (SSO) experience, allowing them to access multiple systems and applications with a single set of credentials. This can improve the user experience and reduce the likelihood of password fatigue and other security issues.
Overall, an effective Identity and Access Management policy is critical to maintaining the security, compliance, and productivity of an organization.
Are There Identity and Access Management Risks?
Identity and Access Management risks refer to potential threats to an organization’s information security caused by the improper management of user identities and access rights to sensitive information and systems.
Some common IAM risks include:
- Weak or compromised passwords: Weak passwords or those that have been compromised through phishing attacks or data breaches can allow unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Lack of access controls: If access controls are not properly implemented or monitored, employees may have access to sensitive information that they do not need to perform their job duties, increasing the risk of data breaches or theft.
- Privilege abuse: Users with excessive access privileges may abuse their access to view or modify sensitive information, steal data or intellectual property, or disrupt critical systems.
- Inadequate authentication and authorization processes: Authentication and authorization mechanisms may be vulnerable to attacks such as spoofing, phishing, or social engineering, allowing unauthorized access to sensitive systems or data.
- Insufficient monitoring and logging: Without proper monitoring and logging, it may be difficult to detect and respond to suspicious activity or security incidents.
- Lack of employee awareness and training: Employees who are not properly trained in IAM best practices may inadvertently expose sensitive information or fall prey to phishing or social engineering attacks.
Third-party risks: Third-party vendors or contractors may have access to sensitive information, and their IAM policies and practices may not align with an organization’s security requirements.
What are Identity and Access Management Best Practices?
A robust Identity and Access Management framework is an essential part of an organization’s information security strategy. Here are some best practices for implementing IAM:
- Implement strong authentication mechanisms: Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all users, including employees, contractors, and third-party vendors. MFA can prevent unauthorized access even if passwords are compromised.
- Follow the principle of least privilege: Grant users only the access necessary to perform their job duties. Avoid granting excessive privileges that could be abused by employees or attackers.
- Use centralized identity management: Implement a centralized identity management system that includes user provisioning and de-provisioning, password management, and access control policies.
- Regularly review and audit access rights: Conduct regular access reviews to ensure that users have only the access they need, and remove access for employees who no longer require it.
- Monitor for suspicious activity: Implement logging and monitoring tools to detect suspicious activity and respond to security incidents promptly.
- Train employees on IAM best practices: Provide regular training and awareness programs for employees on password management, phishing attacks, and other security risks.
- Regularly update IAM policies and procedures: Ensure that IAM policies and procedures are up to date and align with the organization’s security requirements.
- Secure third-party access: Implement appropriate security measures to manage third-party access to sensitive information and systems.
By following these best practices, organizations can better protect their sensitive information and systems from security threats and reduce the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
Does Cyral Offer an Identity and Access Management Solution?
Cyral helps organizations simplify data access management (DAM) and data democratization while embracing zero trust Identity Access and Management, without impacting user experience.
Provision and manage access to all your data stores from any user, application, tool or service using your existing Identity and Access Management solutions. Enrich all activity data with user identity information and apply access control policies uniformly across all service accounts.
Get started in minutes and explore how Cyral can protect your Data Mesh with Data Access Control. You can also contact us to see a live demo.