Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management Definition
Privileged access management (PAM) refers to the tools and technologies that can securely manage user accounts that have elevated privileges to critical systems, databases, or resources. Privileged access management is essentially an identity security solution that functions to prevent credential theft and defend organizations from cyber attacks by monitoring, detecting, and preventing unauthorized privileged access to critical data sources.
Measures such as application access management, privileged session management, shared access password management, and vendor privileged access management all fall under the category of privileged access management.
Privileged Access Management FAQs
What is Privileged Access Management?
Privileged access management comprises the people, procedures, and technologies that enable visibility into who is using privileged accounts and their activity when they are logged in. Robust, modern privileged access management software is able to authenticate any user and any application from anywhere, in a manner that is secure, efficient, and consistent, and then, apply security controls that dictate specific privileges on the data layer.
A major component of PAM is enforcing least privilege access management, which is the concept of restricting access rights and permissions to the bare minimum required for an employee to perform an authorized job function. By limiting the number of users with access to administrative functions, system security can be improved and additional layers of protection can mitigate data breaches.
What types of privileged access management are implemented most commonly? What is privileged access management used for? There are three types of privilege access management needs that most organizations use for on-call access management.
- Standing access, which most companies are trying to reduce because this poses compliance and security risks.
- Rotating access, as is the case with on-call, which most companies are trying to operationalize and automate because of the overhead.
- On-demand access, also described as breakglass or P0, which most companies don’t have tooling for handling.
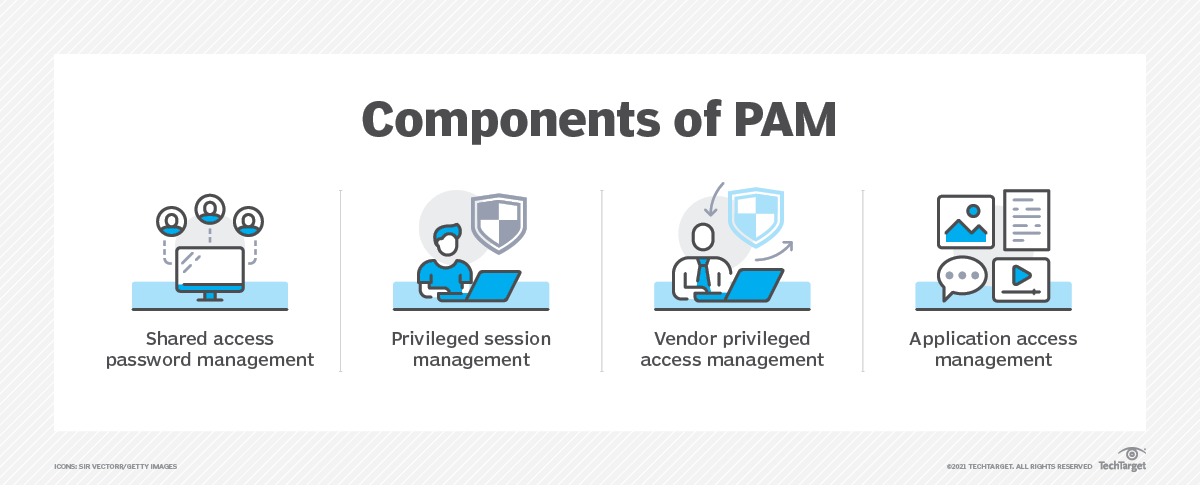
What is the Privileged Access Management Process?
The privileged access management process typically involves implementing the following measures:
- setting up multi-factor authentication (MFA) for admin accounts
- storing permissions and privileged user information in a privileged access management system
- storing secured, privileged passwords in a password vault
- authorized session activity tracking
- reducing insider threats with automated provisioning and deprovisioning
- ensuring organizational compliance with audit logging tools
- dynamically granting authorization and access rights in real-time using attribute-based policies
The Importance of Privileged Access Management
The cause of many malicious cyber activities in an organization are due to privilege abuse. The benefits of privileged access management include: ensuring just-enough and just-in-time privileged access management, enforcing the principle least privilege, enhancing system security, and enabling security teams to take immediate action to mitigate risks. Other crucial benefits of privileged access management include:
- decreases the chances of a security breach; should a breach still occur, PAM decreases its reach in the system
- reduces attack surfaces and entryways for cybersecurity threats by limiting privileges for people, processes, and applications, thereby defending against both internal and external threats
- blocks malware attacks; should malware still gain access, PAM removes excessive privileges that would exacerbate its spread
- simplify audit and compliance requirements by maintaining activity logs, and enabling monitoring that accelerates detection of suspicious activity
- ingests and isolates the credentials of privileged accounts into a secure repository, which reduces the risk of administrator credentials being stolen or misused
- records and logs all activity related to an organization’s critical information technology infrastructures and sensitive corporate data, which helps simplify adhering to privileged access management compliance requirements

Are There Privileged Access Management Risks?
Privileged access management risks lie in the use of insufficient privileged access management vendors for database security. While using PAM to grant database access is advantageous in theory, PAM solutions are not data or database aware, and therefore do not interface with or effectively manage access to data or databases. This negatively impacts everything from security to accessibility.
A traditional privileged access management policy does not provide any audit capabilities beyond the users logging into them to access the database, is not equipped to grant privileges based on who or what is accessing a database, and only focuses on privileged user authentication, leaving out the growing multitude of other applications and microservices accessing databases. Advanced, modern privileged access management services manage database security by enabling privileged access management requirements while enforcing strict security controls.
Identity Access Management vs. Privileged Access Management
While identity access management and privileged access management both involve securing access to sensitive information, they differ slightly in their approach. Where identity access management functions to identify and authorize users across an entire organization, privileged access management serves as a subset of identity access management that specifically focuses on permissions for privileged users that need access to more sensitive data.
What are the Privileged Access Management Best Practices?
Some common privileged access management best practices that will help ensure that PAM implementations are effective include:
- Maintain a log of all privileged accounts, and track and document all changes.
- Disable account sharing amongst administrators.
- Mandate that each administrator only maintains one personal privileged account.
- Institute password policies.
- Eliminate all default passwords on all company devices.
- Schedule regular password updates for privileged accounts.
- Institute two-factor authentication for privileged accounts.
- Limit granted access privileges to the resource by limiting permissions scope.
- Enforce separation of duties among team members to ensure that no one employee is granted enough privileges to misuse the system on their own.
- Enforce the principle of least privilege.
- Invest in logging and monitoring tools and techniques to get a comprehensive view of privileged users’ activities.
- Ensure employees are aware of current privileged access policies and procedures, and understand how to properly manage their credentials.
- Maintain documentation of account management rules and procedures.
- Mandate that account management rules and procedures are verified by company leaders.
Does Cyral Offer a Privileged Access Management Solution?
A robust privileged access management tool should be able to balance security with the authentication, authorization, and auditing needs of an organization, while connecting more data consumers with more data sources and still minimizing the risk of threats infiltrating the database. Cyral’s privileged access management solution achieves this balance, effectively and consistently authenticating and authorizing users’ access while also applying strict security controls. Cyral operationalizes and automates standing, rotating, and on-demand privileged access management; limits activity based on customer-defined policies; creates audit artifacts; and captures rich activity logs complete with user identity.

The ideal solution for database privileged access management is not imaginary. It’s Cyral. Contact us about arranging a demonstration.