
Data Privacy Management
Protect your Customers’ Personal Data
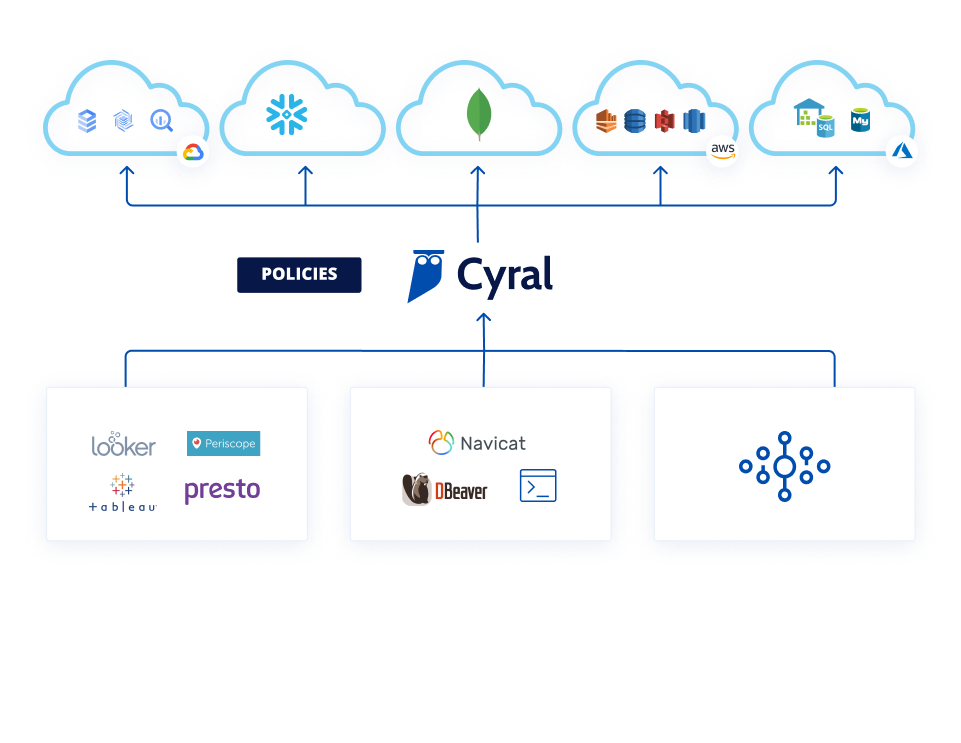
Easily discover and classify personal data in databases and data lakes. Enforce granular access controls for data masking and filtering.
Secure PII Data in Databases
and Data Lakes
Use granular policies to mask and filter data
Implement controls for both users and applications
Automatically discover and classify any new data
Unified, Policy-based Privacy Management
Data Masking
- Mask PII data in databases and data lakes
- Implement nulling, redaction and substitution
Data Filtering
- Filter rows and documents from results
- Enable access to records based on their value
Easy to get Started and Simple to Maintain
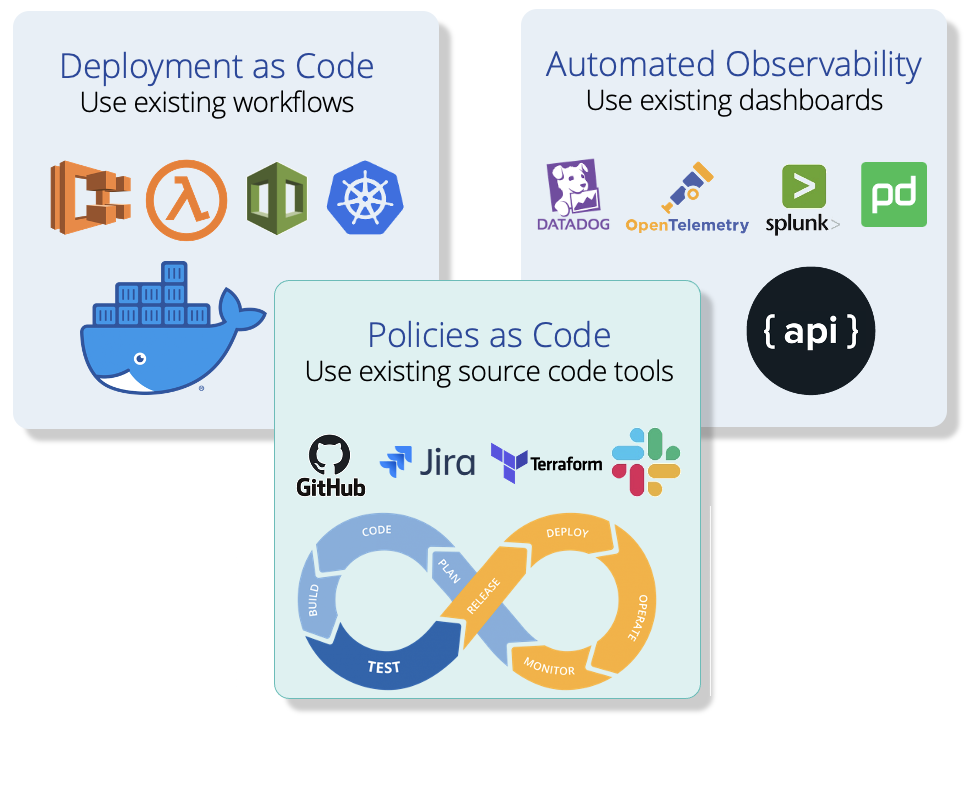
Deploy in minutes
- No need to create and manage custom views
- No change to data models or user workflows
Implement policies as code
- Codify privacy policies, providing visibility and clear tracking
- Enforce continuous application of policies by integrating with your CI/CD pipeline
Terminology
Terminology
Differential privacy
As companies become more data driven, data privacy becomes a greater priority. Differential privacy is a powerful tool for quantifying and solving practical problems related to privacy. Its flexible definition gives it the potential to be applied in a wide range of applications. Differential privacy makes it possible for tech companies to collect and share aggregate information about user habits, while maintaining the privacy of individual users.
Wikipedia describes it as “A system for publicly sharing information about a dataset by describing the patterns of groups within the dataset while withholding information about individuals in the dataset. The idea behind differential privacy is that if the effect of making an arbitrary single substitution in the database is small enough, the query result cannot be used to infer much about any single individual, and therefore provides privacy.”
“Another way to describe differential privacy is as a constraint on the algorithms used to publish aggregate information about a statistical database which limits the disclosure of private information of records whose information is in the database. For example, differentially private algorithms are used by some government agencies to publish demographic information or other statistical aggregates while ensuring confidentiality of survey responses, and by companies to collect information about user behavior while controlling what is visible even to internal analysts.”
Security as Code
Security as Code is the methodology of codifying security and policy decisions. Security testing and scans are implemented into your CI/CD pipeline to automatically and continuously detect vulnerabilities and security bugs. Access policy decisions are codified into source code allowing everyone across the organization to see exactly who has access to what resources.
GDPR
General Data Protection Regulations, more commonly referred to as GDPR, is a legal framework that sets guidelines for the collection and processing of personal information from citizens of the European Union (EU). Since the Regulation applies regardless of where websites are based, it must be heeded by all sites that attract European visitors, even if they don’t specifically market goods or services to EU residents.
The GDPR mandates that EU visitors be given a number of data disclosures. The site must also take steps to facilitate such EU consumer rights as a timely notification in the event of personal data being breached. Adopted in April 2016, the Regulation came into full effect in May 2018, after a two-year transition period.
CCPA
According to the State of California Department of Justice, the California Consumer Privacy Act of 2018 (CCPA) gives consumers more control over the personal information that businesses collect about them and the CCPA regulations provide guidance on how to implement the law. This landmark law secures new privacy rights for California consumers, including:
- The right to know about the personal information a business collects about them and how it is used and shared;
- The right to delete personal information collected from them (with some exceptions);
- The right to opt-out of the sale of their personal information; and
- The right to non-discrimination for exercising their CCPA rights.
Businesses are required to give consumers certain notices explaining their privacy practices. The CCPA applies to many businesses, including data brokers.
LGPD
The Brazilian General Data Protection Law (Lei Geral de Proteção de Dados Pessoais or LGPD) is a new law that was passed by the National Congress of Brazil on August 14, 2018 and came into effect on August 15, 2020.
The LGPD creates a legal framework for the use of personal data of individuals in Brazil, regardless of where the data processor is located. It is closely modeled after the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and like GDPR, the LGPD has far reaching consequences for data processing activities in and outside of Brazil. >earn more about LGDP.
Ready to Get Started?
Get started in minutes and explore how Cyral can protect your Data Mesh. You can also contact us to schedule a live demo for a custom data privacy management solution. Feel secure with a strong data privacy management system you can rely on.

