Varonis acquires Cyral
Varonis' Data Security Platform now includes next-generation Database Activity Monitoring (DAM), with the acquisition of Cyral, accelerating our mission to deliver AI-powered data security for all data, everywhere.
- Agentless
- Robust
- Cloud & on-prem

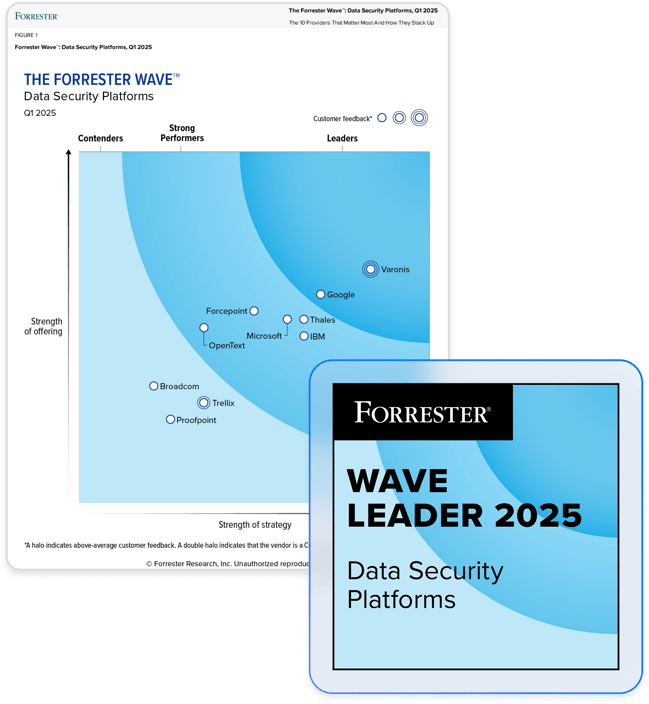
Partner with the leader in data security.
Legacy DAM is dead.
Organizations struggle to secure thousands of managed, unmanaged, and on-prem databases storing their most critical PII, intellectual property, and AI training data. Lack of competition and complex barriers to entry have stifled innovation in the DAM market. The AI era demands a new and novel approach to database security.
By combining Cyral's cloud-native DAM with Varonis' robust and growing database security capabilities, customers can begin to upgrade their costly legacy solutions and shatter the silos that have traditionally separated structured and unstructured data security.
Agentless, context-rich activity monitoring
Get real-time database activity with zero performance impact across on-prem and cloud data sources. Activity is enriched with end-user identity and session context to detect anomalies and simplify audits.
Identity federation
Enable single sign-on and MFA across all databases using existing IDPs, eliminating the need for shared credentials.
Fine-grained policy enforcement
Centralize just-in-time authorization policies, down to the row, column, or object level, using IAM roles and dynamic, attributed-based access.
User-to-data tracking
Resolve service account queries to the individual user behind the app or tool providing access to prevent abuse and provide more detailed auditing.
Companies today are embracing cloud-based data services to make data accessible by everyone. But this leaves them blind to who has access to what data?
Cyral solves this problem with a new approach that delivers visibility, access management and protection for the data cloud.
“Varonis' acquisition of Cyral brings together a shared vision for securing customers' data end-to-end as AI ushers in a new era of growth and innovation. The lifeblood of AI is data, and Varonis is leading the charge by driving automated data security outcomes at scale.”
Manav Mital
Cyral Co-Founder and CEO
Read announcementDatabase security resources
Ready to see the #1 Data Security Platform in action?
Ready to see the #1 Data Security Platform in action?
“I was amazed by how quickly Varonis was able to classify data and uncover potential data exposures during the free assessment. It was truly eye-opening.”
Michael Smith, CISO, HKS
"What I like about Varonis is that they come from a data-centric place. Other products protect the infrastructure, but they do nothing to protect your most precious commodity — your data."
Deborah Haworth, Director of Information Security, Penguin Random House
“Varonis’ support is unprecedented, and their team continues to evolve and improve their products to align with the rapid pace of industry evolution.”
Al Faella, CTO, Prospect Capital


